Administrative centers have historically served as the nerve centers of empires, acting as the focal points for governance, resource allocation, and the implementation of imperial policies. These centers were often strategically located to facilitate control over vast territories, enabling rulers to exert influence over diverse populations. For instance, the Roman Empire established cities like Rome and Constantinople as administrative hubs, where bureaucratic functions were centralized.
These cities not only housed the imperial court but also served as the headquarters for various administrative functions, including tax collection, legal adjudication, and military coordination. The significance of administrative centers extends beyond mere governance; they were also cultural melting pots that reflected the empire’s diversity. In places like Alexandria, Egypt, the convergence of different cultures led to a flourishing of knowledge and arts.
The presence of libraries, schools, and temples in these centers fostered intellectual exchange and innovation. This cultural dynamism was crucial for maintaining the loyalty of various ethnic groups within the empire, as it provided a sense of shared identity and purpose. Thus, administrative centers were not just functional entities; they were vital to the cohesion and stability of empires.
Key Takeaways
- Administrative centers play a crucial role in governing and managing empires, serving as hubs for political, economic, and social activities.
- The presence of administrative centers often leads to the growth and development of urban areas, as they attract people and resources, contributing to urbanization.
- Infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and public buildings are developed in administrative centers to support the growing population and facilitate governance.
- Urbanization resulting from administrative centers can have both positive and negative social and economic effects, such as increased wealth disparity and cultural exchange.
- Administrative centers are closely linked to political power, as they serve as the seat of government and influence decision-making, shaping the empire’s policies and governance.
- The legacy of urbanization in empires can be seen in the lasting impact on architecture, culture, and governance, shaping the development of future societies.
The Impact of Administrative Centers on Urbanization
The establishment of administrative centers often catalyzed urbanization, transforming small settlements into bustling cities. As these centers attracted officials, merchants, and laborers, they became hubs of economic activity. The influx of people seeking opportunities led to the rapid growth of urban populations.
For example, during the height of the Ottoman Empire, cities like Istanbul expanded significantly as they became administrative and commercial centers. The concentration of resources and services in these urban areas created a dynamic environment that encouraged further migration and settlement. Moreover, administrative centers played a crucial role in shaping urban infrastructure.
The need for efficient governance and service delivery prompted the development of roads, public buildings, and marketplaces. In ancient Mesopotamia, for instance, the rise of city-states like Uruk was closely linked to their role as administrative centers. The construction of ziggurats not only served religious purposes but also functioned as administrative buildings where officials could conduct business.
This infrastructure laid the groundwork for future urban development, establishing patterns that would influence city planning for centuries to come.
The Development of Infrastructure in Administrative Centers
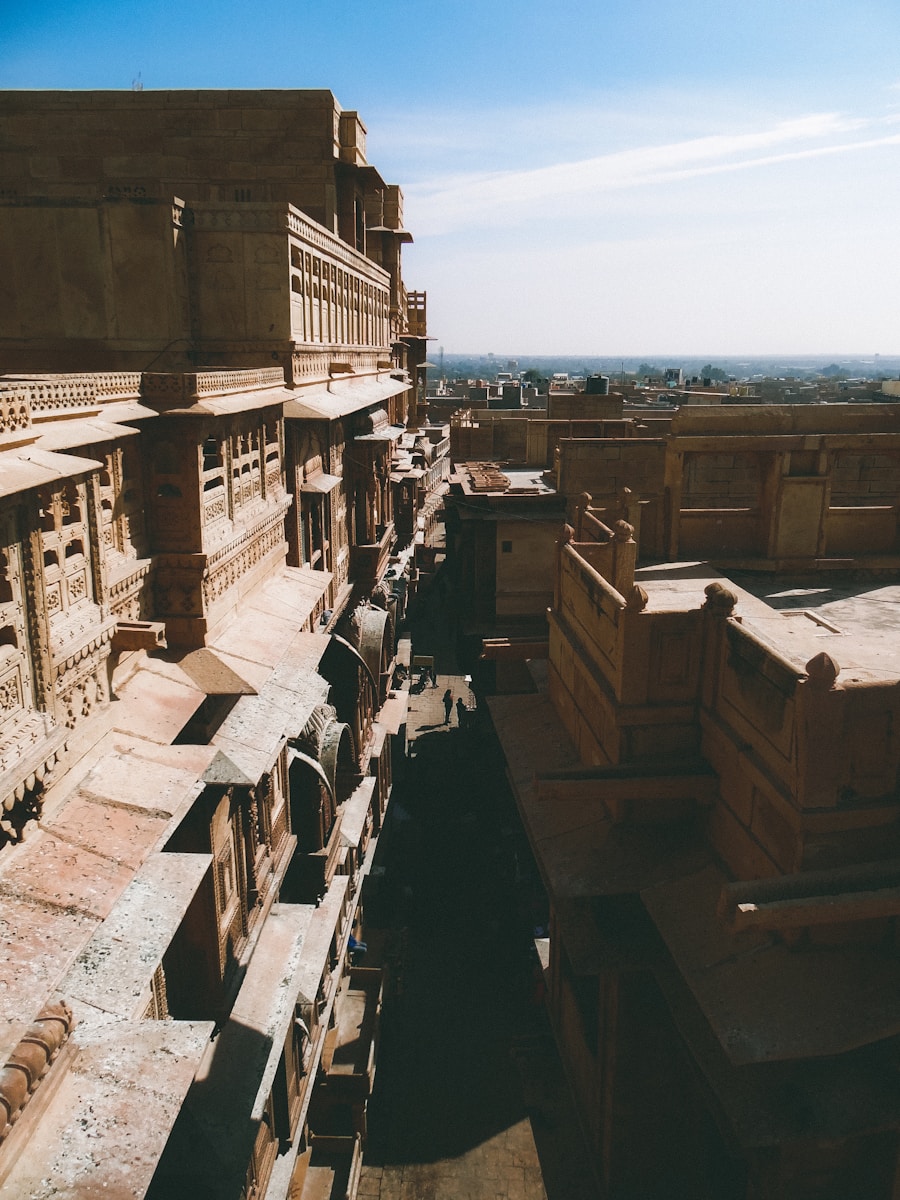

Infrastructure development in administrative centers was essential for facilitating trade, communication, and governance.
The Roman Empire is a prime example of this phenomenon; its extensive network of roads allowed for rapid military mobilization and trade across Europe, North Africa, and parts of Asia.
The saying “All roads lead to Rome” encapsulates the importance of these routes in linking various parts of the empire to its administrative heart. In addition to transportation infrastructure, administrative centers often featured monumental architecture that symbolized imperial power and authority. Structures such as palaces, government buildings, and public squares were designed not only for functionality but also to convey the grandeur of the empire.
The construction of the Parthenon in Athens served both religious and civic purposes while showcasing the city-state’s wealth and cultural achievements. Such architectural endeavors were instrumental in reinforcing the legitimacy of rulers and fostering a sense of pride among citizens.
The Social and Economic Effects of Urbanization in Empires
Urbanization driven by administrative centers had profound social and economic effects on empires. As cities grew, they became melting pots of diverse cultures, leading to increased social interaction and exchange. This cultural amalgamation often resulted in new social dynamics, including shifts in class structures and the emergence of new social groups.
In medieval Europe, for instance, the rise of towns as administrative centers contributed to the decline of feudalism by creating a burgeoning merchant class that challenged traditional power hierarchies. Economically, urbanization facilitated specialization and division of labor. As cities became centers of commerce and trade, individuals could focus on specific trades or crafts rather than subsistence agriculture.
This specialization led to increased productivity and innovation. In ancient China, the development of cities along the Silk Road allowed for the exchange of goods such as silk, spices, and ceramics. The economic prosperity generated by these trade networks not only enriched urban centers but also contributed to the overall wealth of the empire.
The Relationship Between Administrative Centers and Political Power
The relationship between administrative centers and political power is intricate and multifaceted. Administrative centers often served as symbols of authority, where rulers could project their power and influence over their subjects. The concentration of political functions in these centers allowed for more effective governance but also created vulnerabilities.
For instance, during times of political upheaval or rebellion, control over these centers became crucial for maintaining stability within the empire. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked a significant shift in power dynamics, illustrating how control over an administrative center could determine the fate of an empire. Furthermore, administrative centers often became battlegrounds for competing factions within empires.
Rivalries among local elites or external threats could lead to conflicts that destabilized these critical hubs. In ancient Rome, power struggles among generals often centered around control of key cities like Rome itself or Alexandria. Such conflicts not only affected governance but also had far-reaching implications for trade and social order within the empire.
The Legacy of Urbanization in Empires
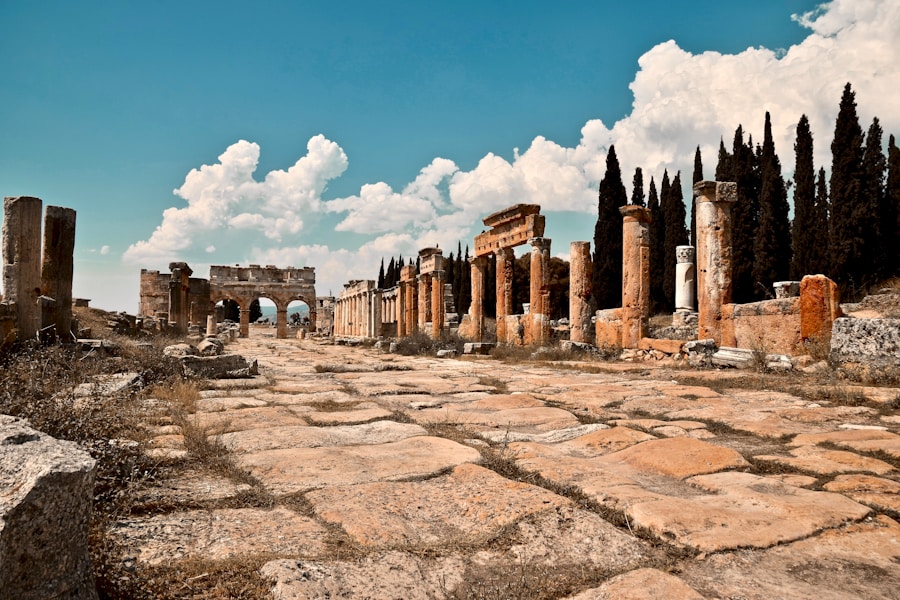

The legacy of urbanization driven by administrative centers is evident in contemporary societies around the world. Many modern cities trace their origins back to ancient administrative hubs that evolved over centuries.
Moreover, the patterns established by ancient urbanization continue to influence modern urban planning and governance. The principles of infrastructure development, zoning regulations, and public services can be traced back to practices initiated in these early administrative centers. As cities grapple with contemporary challenges such as population growth and sustainability, understanding the historical context of urbanization can provide valuable insights into effective governance strategies.
In conclusion, administrative centers have played a pivotal role in shaping empires throughout history. Their influence on urbanization, infrastructure development, social dynamics, political power structures, and lasting legacies underscores their significance in understanding the complexities of human civilization. As we examine these historical narratives, we gain a deeper appreciation for how these centers have shaped not only past empires but also our present-day societies.
Administrative centers played a crucial role in the rise of urbanization in ancient empires, as explored in a fascinating article on Mimamsa School. This article delves into the philosophical concepts of perception and knowledge, shedding light on how these ideas influenced the development of administrative structures in ancient civilizations. Understanding the interplay of moral rights, duties, and virtue is also essential in comprehending the societal dynamics that shaped urban centers, as discussed in another thought-provoking article on social ethics. Additionally, technology has played a significant role in modern administrative centers, as highlighted in a comprehensive guide on technology job boards, showcasing how advancements in tech have transformed the way administrative tasks are carried out in contemporary urban settings.
FAQs
What are administrative centers in empires?
Administrative centers in empires are the central hubs where the government and administrative functions of the empire are carried out. These centers often house the imperial palace, government offices, and other important institutions.
How did administrative centers contribute to the rise of urbanization in empires?
Administrative centers often attracted a large population of government officials, bureaucrats, and support staff, leading to the growth of urban areas around these centers. The concentration of political and administrative power in these centers also attracted merchants, artisans, and other individuals seeking economic opportunities, further contributing to urbanization.
What are some examples of administrative centers in historical empires?
Examples of administrative centers in historical empires include Persepolis in the Achaemenid Empire, Chang’an in the Han Dynasty of China, and Constantinople in the Byzantine Empire. These centers served as the political, economic, and cultural heart of their respective empires.
How did the development of administrative centers impact the social and cultural dynamics of empires?
The development of administrative centers often led to the convergence of diverse populations, resulting in the exchange of ideas, languages, and cultural practices. This cultural interaction and diversity contributed to the richness and complexity of urban life in these centers.
What role did administrative centers play in the governance and control of empires?
Administrative centers served as the nerve centers of imperial governance, where decisions regarding taxation, law enforcement, infrastructure development, and military operations were made. The proximity of government institutions and officials in these centers facilitated efficient governance and control over the empire.



















+ There are no comments
Add yours