Exploring the Mysterious Roche Limit
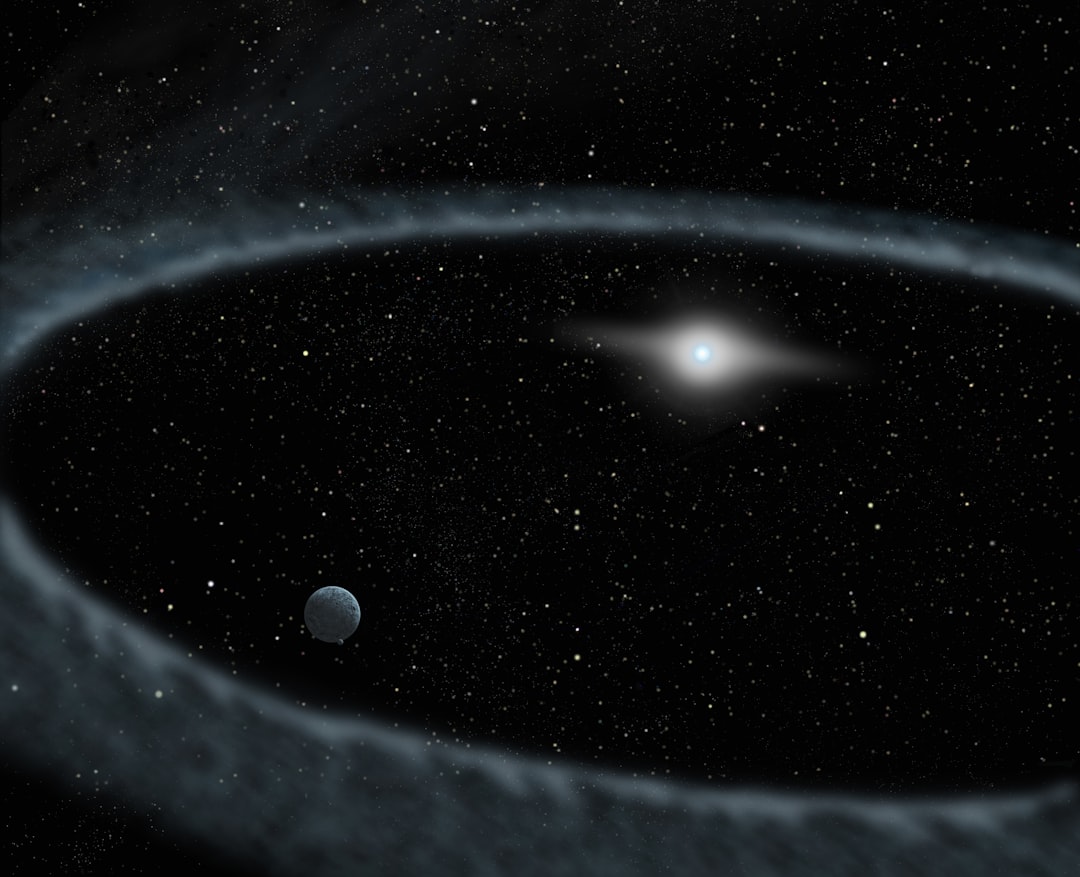
The Roche Limit is a critical concept in astrophysics that defines the minimum distance at which a celestial body, such as a moon or a satellite, can orbit a larger body without being torn apart by tidal forces. Named after the French astronomer Édouard Roche, who first described it in [more ...]
Protect Yourself from Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks have become a prevalent threat in the digital landscape, targeting individuals and organizations alike. These attacks typically involve deceptive tactics aimed at tricking victims into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, or personal identification details. Cybercriminals often masquerade as trustworthy entities, using familiar logos and [more ...]
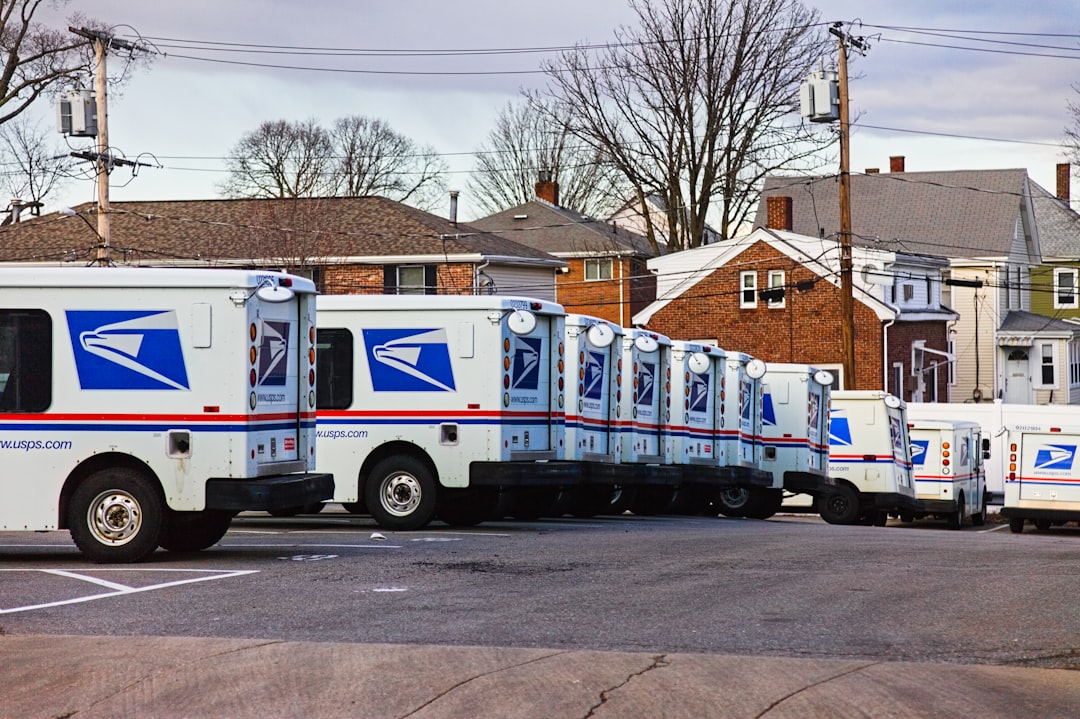
Exploring US Postal Service Jobs: Opportunities and Careers
The United States Postal Service (USPS) has long been a cornerstone of American society, providing essential mail and package delivery services across the nation. Established in 1775, the USPS has evolved significantly over the centuries, adapting to technological advancements and changing consumer needs. Today, it remains one of the largest [more ...]
Exploring the Mysteries of Trans-Neptunian Objects
Trans-Neptunian Objects (TNOs) are celestial bodies located in the outer reaches of our solar system, beyond the orbit of Neptune. This region, often referred to as the Kuiper Belt, is home to a diverse array of objects, including dwarf planets, comets, and other icy bodies. TNOs are significant not only [more ...]