Category: Social Sciences
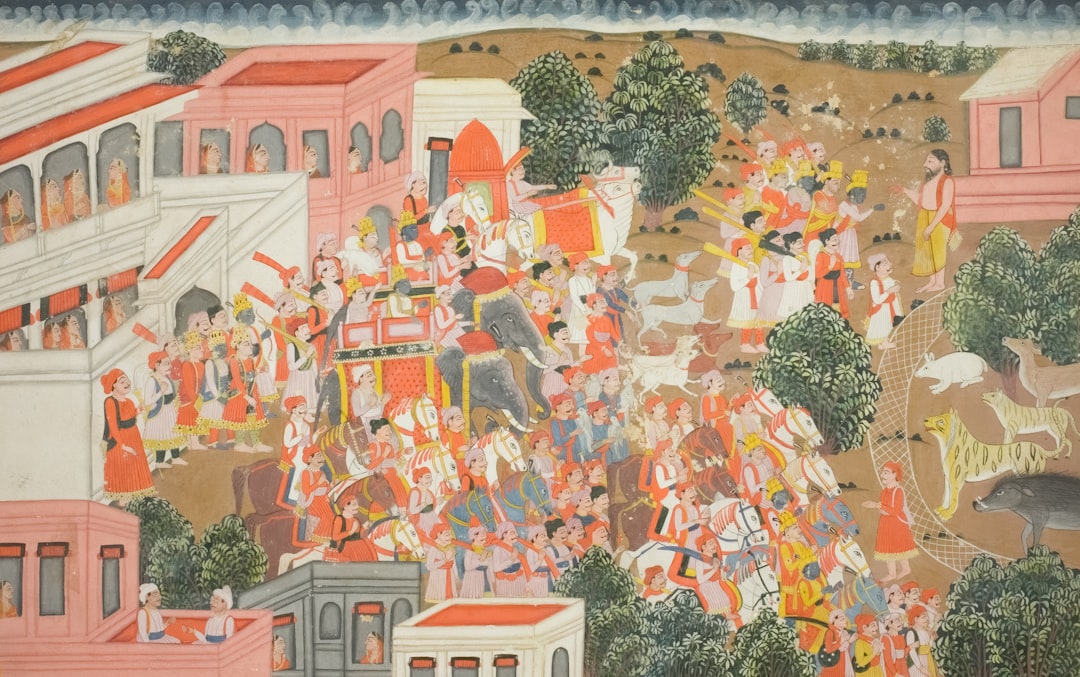
Sculptural Art: Iconography and Meaning
Sculptural art has a rich and varied history that spans thousands of years, reflecting the evolution of human thought, culture, and expression. From the ancient [more…]
Hindu Temples: Vastupurush and Cosmic Symbolism
Hindu temples serve as significant cultural and spiritual centers within the Hindu tradition. They are not merely places of worship but also embody the rich [more…]
Arches, Domes, and Vaults in Design
The use of arches, domes, and vaults in architecture can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where they served both structural and aesthetic purposes. The [more…]
Understanding Architecture: Plans and Structures
Architectural plans serve as the foundational blueprint for any construction project, whether it be residential, commercial, or public infrastructure. These plans are essential for translating [more…]
Urbanization and Its Economic Impact
Urbanization refers to the increasing population shift from rural to urban areas, a phenomenon that has been accelerating since the Industrial Revolution. This process involves [more…]
Demographic Shifts During the Colonial Period
Colonial demographics refer to the study of population characteristics during the colonial period, particularly in regions that experienced European colonization from the 15th to the [more…]
Foreign Capital Investment in Transport
Foreign capital investment refers to the flow of funds from one country to another, where investors seek to acquire assets or establish business operations. This [more…]
Roadways and Railways in Colonial India
The transportation infrastructure of colonial India fundamentally altered the subcontinent’s socio-economic structure. The British colonial administration established and expanded roadways and railways to facilitate the [more…]
Industrial Growth in a Colonial Economy
The colonial economy encompasses the economic systems established by European powers in their overseas territories from the 16th to the 20th centuries. These systems prioritized [more…]
Banking, Currency, and Insurance Developments
The banking sector has experienced significant technological transformation over recent decades. Online banking platforms have fundamentally changed customer-bank interactions, enabling consumers to conduct transactions such [more…]
Internal and External Trade Under British Rule
The period of British colonial rule in India, spanning from the mid-18th century to the mid-20th century, marked a significant transformation in the country’s trade [more…]
Emergence of New Industries in Colonial India
Colonial India refers to the period of British dominance over the Indian subcontinent from the mid-18th century to 1947. The British East India Company began [more…]
Irrigation, Famine, and Rural Debt in India
Irrigation plays a pivotal role in Indian agriculture, serving as a lifeline for millions of farmers across the country. With approximately 60% of India’s agricultural [more…]
World Depression and Its Agricultural Impact
World depression, often characterized by a significant decline in economic activity across nations, has roots that can be traced to a multitude of factors. One [more…]
Commercialization of Indian Agriculture
Indian agriculture has a rich and diverse history that dates back thousands of years. The Indus Valley Civilization, which flourished around 2500 BCE, is one [more…]
Land Revenue Settlements: Permanent to Ryotwari
Land revenue settlements fundamentally transformed agricultural practices and land ownership structures across various regions, with particularly significant impact in India. The British colonial administration implemented [more…]
Impact of Colonial Economy on India
The colonial economy in India, established during British rule from the mid-18th century until the mid-20th century, was characterized by a systematic exploitation of the [more…]
Drain of Wealth Under Early Colonial Rule
The concept of “drain of wealth” describes the systematic transfer of resources, capital, and economic value from one region or country to another, typically through [more…]
Mercantilism and the Decline of Traditional Industries
Mercantilism emerged as a dominant economic theory in Europe from the 16th to the 18th centuries, fundamentally reshaping the landscape of trade and commerce. This [more…]
Colonialism, Imperialism, and Economic Historiography
Colonialism, a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, has shaped the course of human history for centuries. It refers to the practice of acquiring control over foreign [more…]
Economic Regulations in Revenue and Finance
Economic regulations play a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of revenue and finance within a nation. These regulations are designed to govern the economic [more…]
Taxation: From Tribute to Uniform Land Tax
Taxation has undergone a profound transformation throughout history, evolving from primitive systems of tribute to the more structured and equitable frameworks we see today, such [more…]
Land Grants and the Feudal Economy
Land grants have played a pivotal role in shaping the socio-economic structures of various civilizations throughout history, particularly during the feudal era in medieval Europe. [more…]
Origin and Growth of Feudalism in India
Feudalism in India represents a complex and multifaceted system that evolved over centuries, deeply intertwined with the socio-political fabric of the subcontinent. Unlike the European [more…]
Communication Systems in Early Trade
Communication served as the backbone of early trade, facilitating the exchange of goods, services, and ideas among diverse cultures. In ancient societies, where barter was [more…]
Role of Guilds in Economic Activity
The origins of guilds can be traced back to the medieval period in Europe, particularly during the 11th and 12th centuries. These organizations emerged as [more…]
Trade Routes and Transportation Networks
Throughout history, trade routes have served as the arteries of commerce, facilitating the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas across vast distances. The Silk Road, [more…]
Inland and Foreign Trade in Ancient India
Ancient India was a vibrant hub of commerce, characterized by a complex network of inland and foreign trade that flourished for centuries. The subcontinent’s geographical [more…]
Ownership Patterns in Ancient India
Ownership patterns in ancient India were deeply intertwined with the socio-economic and cultural fabric of the time. The concept of ownership was not merely a [more…]
State Role in Land Grants and Boundaries
The concept of land grants has deep historical roots, tracing back to ancient civilizations where land was often allocated by rulers to individuals or groups [more…]
The Impact of Art on Mental Health: A Study in Humanities and Social Sciences
The intersection of art and mental health has garnered increasing attention in recent years, as researchers and practitioners alike explore the profound effects that artistic [more…]
Demarcation and Disputes Over Land
Demarcation refers to the process of establishing the boundaries of a piece of land, which is crucial for defining ownership and usage rights. This process [more…]
Exploring the Value of a Suss Degree
The SUSS degree, offered by the Singapore University of Social Sciences, is designed to cater to the evolving educational needs of adult learners and working [more…]
Communal, Royal, and Individual Land Systems
Communal land systems are characterized by collective ownership and management of land resources by a community rather than by individuals. This system is often rooted [more…]
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Retail: IJRISs
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in the retail sector, reshaping how businesses operate and interact with consumers. The integration of AI [more…]
Evolution of Farming in Ancient India
The agricultural history of India is a tapestry woven with the threads of diverse cultures, climatic conditions, and innovative practices that have evolved over millennia. [more…]
Sorokin’s Impact on Modern Sociology
Pitirim Aleksandrovich Sorokin, a prominent figure in the field of sociology, emerged as a significant intellectual force in the early to mid-20th century. Born in [more…]
Agricultural Processes and Irrigation Methods
Agriculture is a cornerstone of human civilization, serving as the primary means of food production and resource management. The processes involved in agriculture are multifaceted, [more…]
The Impact of Sociology on Organizational Behavior
Sociology, as a discipline, delves into the intricate web of social relationships, institutions, and structures that shape human behavior. It provides a framework for understanding [more…]
Techniques and Crop Patterns of Settled Farming
Settled farming, often referred to as sedentary agriculture, marks a significant shift in human history from nomadic lifestyles to permanent agricultural communities. This transition, which [more…]
The Impact of Social Science in Understanding Human Behavior
Social science is a broad field that encompasses various disciplines aimed at understanding the complexities of human behavior and societal structures. It includes areas such [more…]
Bronze and Iron in Early Agriculture
The advent of metallurgy marked a pivotal moment in human history, particularly in the realm of agriculture. The transition from the Stone Age to the [more…]
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
In the contemporary digital landscape, social media has become an integral part of daily life for billions of individuals worldwide. Platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, [more…]
Trade Routes and Interactions with Neighboring Regions
Trade routes have been the lifeblood of commerce and cultural exchange throughout human history. These pathways, whether over land or sea, have facilitated the movement [more…]
Aligarh Movement and Modern Muslim Reform
The Aligarh Movement emerged in the late 19th century as a response to the socio-political challenges faced by Muslims in India, particularly following the decline [more…]
Women in Politics and Economy: Socio-Legal Progress
The quest for women’s political and economic rights has been a long and arduous journey, marked by significant milestones and relentless advocacy. Historically, women have [more…]
Exploring the Intersection of Social Science and Social Studies
Social science serves as the backbone of social studies education, providing a framework through which students can explore the complexities of human behavior, societal structures, [more…]
Reform and Women’s Emancipation: A Critical Reading
The journey toward women’s emancipation is deeply rooted in a complex historical context that spans centuries and continents. In many societies, women have been relegated [more…]
Arya Samaj, Theosophical Society, and Beyond
The Arya Samaj was founded in 1875 by Swami Dayananda Saraswati, a prominent figure in the Indian reform movement. His vision was to return to [more…]
Exploring Social Dynamics: A Group Observation Activity
Social dynamics is a multifaceted field that examines the interactions and behaviors of individuals within groups. It encompasses a wide range of phenomena, from the [more…]
Emerging Themes in Gender Studies: Issues and Innovations
Intersectionality is a critical framework that emerged from feminist theory, primarily articulated by legal scholar Kimberlé Crenshaw in the late 1980s. It posits that individuals [more…]
Brahma Samaj and Socio-Religious Reform
The Brahma Samaj, a significant socio-religious reform movement in India, emerged in the early 19th century as a response to the prevailing social and religious [more…]
Development of Gender Research in Indian Historiography
The exploration of gender within Indian historiography has its roots in the early 20th century, a period marked by the emergence of nationalist movements and [more…]
The Impact of Social Research on Sociology
Social research serves as a cornerstone of sociology, providing the empirical foundation upon which sociological theories and insights are built. It encompasses a wide array [more…]
Constitutional Rights of Women: History and Debates
The constitutional rights of women represent a critical aspect of the broader human rights discourse, encapsulating the legal frameworks that protect and promote gender equality. [more…]
Christian Missionaries and Indian Social Life
The arrival of Christian missionaries in India can be traced back to the early centuries of the Common Era, with the most notable figure being [more…]
Examining the Impact of Cultural Factors on Social Behavior
Cultural factors play a pivotal role in shaping social behavior, influencing how individuals interact with one another within their communities. These factors encompass a wide [more…]
Women and Environment: Linking Struggles and Rights
The relationship between women’s rights and environmental issues is increasingly recognized as a critical area of study and activism. At its core, this intersection highlights [more…]
Social Transformation Through Economic Change
The intricate relationship between social transformation and economic change is a subject of considerable academic and practical interest. At its core, social transformation refers to [more…]
Women’s Liberation Movements: Voices of Change
The roots of women’s liberation movements can be traced back to the early 19th century, a period marked by significant social and political upheaval. The [more…]
Exploring the Impact of MSocSc on Social Science Research
The Master of Social Science (MSocSc) is an advanced academic degree that focuses on the study of social phenomena, human behavior, and the complex interactions [more…]
History of Feminism: From Rights to Revolution
The origins of feminism can be traced back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, a period marked by significant social upheaval and the [more…]
Middle Class Role in India’s Modernization
The middle class plays a pivotal role in the economic landscape of any nation, serving as a crucial engine for growth and development. In many [more…]
The Importance of Social Science in Understanding Society
Social science is a broad field that encompasses the study of human behavior, social structures, and the various factors that influence interactions within societies. It [more…]
Tracing Women’s Status Across India’s Historical Phases
The status of women in India has undergone significant transformations throughout its history, shaped by cultural, social, and political influences. From ancient times to the [more…]
Emergence of the Working and Middle Classes
The historical evolution of the working and middle classes is a complex narrative that intertwines with the broader socio-economic transformations of society. The origins of [more…]
Women in Northeast India: A Unique Historical Lens
Northeast India, a region characterized by its rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and ethnicities, is home to a diverse population of women who play pivotal [more…]
Understanding Society: The Power of Doing Sociology
Sociology is the systematic study of society, social institutions, and social relationships. It seeks to understand how human behavior is shaped by social structures, cultural [more…]
Pre-Colonial and Colonial India: Shifts in Women’s Roles
In pre-colonial India, the roles of women were deeply intertwined with the socio-cultural fabric of society. Women were primarily seen as custodians of family values [more…]
Capitalism’s Growth in Indian Agriculture
Agriculture in India has a rich and diverse history that dates back thousands of years. The Indus Valley Civilization, which flourished around 2500 BCE, is [more…]
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: A Contemporary Social Science Perspective
In the contemporary landscape, social media has become an omnipresent force, shaping not only how individuals communicate but also how they perceive themselves and their [more…]
Women’s Position in Early India: Power and Limits
The status of women in early India is a complex tapestry woven from various threads of cultural, religious, and social influences. The Vedic period, which [more…]
Rise of the Press and New Intelligentsia
The history of the press is a fascinating narrative that traces the evolution of communication and information dissemination from ancient times to the modern era. [more…]
Understanding Gender: Nature vs. Culture
The discourse surrounding gender has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from a binary understanding rooted in biological determinism to a more nuanced [more…]
The Impact of BSocSc on Social Sciences
The Bachelor of Social Science (BSocSc) is an academic degree that has gained prominence in the landscape of higher education, particularly in the realm of [more…]
Feminism and Cultural Dichotomy: A Gender Perspective
Feminism, as a social and political movement, has evolved through various waves, each characterized by distinct goals and ideologies. The first wave, which emerged in [more…]
Growth of Modern Education: 1813–1947
The period from 1813 to 1947 marks a significant transformation in the landscape of education, particularly in the Western world. This era witnessed the transition [more…]
Exploring Asian Social Science: Understanding Cultural Dynamics
Asian social science encompasses a vast and intricate tapestry of disciplines that examine the myriad social, cultural, economic, and political phenomena across the continent. This [more…]
Patriarchy, Patriliny, Matriarchy, and Matriliny Explained
Patriarchy is a social system characterized by male dominance, where men hold primary power and authority in various aspects of life, including politics, economics, and [more…]
Patriarchy, Patriliny, Matriarchy, and Matriliny Explained
Patriarchy is a social system characterized by the predominance of male authority and power in various aspects of life, including family, politics, and economics. This [more…]
Modernization and Secularization in India
Modernization and secularization are two interlinked processes that have significantly shaped the socio-political landscape of India over the past century. Modernization refers to the transformation [more…]
Concept of Gender: Beyond Male and Female
Gender identity is a deeply personal and intrinsic sense of one’s own gender, which may or may not align with the sex assigned at birth. [more…]
Exploring Social Science Courses in University
Social science courses encompass a broad spectrum of academic disciplines that explore the complexities of human behavior, societal structures, and cultural dynamics. These courses are [more…]
Modern Indian Historiography: From Empire to People
Modern Indian historiography is a complex tapestry woven from diverse threads of cultural, political, and social narratives that have evolved over centuries. The study of [more…]
Sanskritization and Westernization Explained
Sanskritization and Westernization are two significant sociocultural processes that have shaped societies, particularly in the context of India and its diaspora. Sanskritization refers to the [more…]
Understanding Human Behavior: The Intersection of Social and Political Sciences
Human behavior is a complex tapestry woven from a multitude of threads, including biological, psychological, social, and environmental factors. It encompasses the myriad ways in [more…]
Marxist and Subaltern Views: Rewriting Modern Indian History
The interplay between Marxist and subaltern perspectives has significantly shaped the discourse surrounding Indian history and society. Marxism, rooted in the works of Karl Marx [more…]
Understanding Social History’s Evolution
Social history emerged as a distinct field of study in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, primarily as a reaction against the traditional political [more…]
Nationalist Historiography: Reclaiming India’s Past
The emergence of nationalist historiography in India can be traced back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, a period marked by the struggle [more…]
Advancing Social Sciences: The Academy’s Impact
Social sciences encompass a broad range of disciplines, including sociology, psychology, anthropology, economics, and political science, each contributing uniquely to our understanding of human behavior [more…]
Colonial and Imperialist Historiography: The Cambridge School
Colonial and imperialist historiography encompasses the study of historical narratives that focus on the processes, impacts, and legacies of colonialism and imperialism. This field of [more…]
Historiography of Social Change in India
Historiography, the study of historical writing and the methods of historians, serves as a critical lens through which we can examine the evolution of societies [more…]
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: A Mixed-Methods Study
In the contemporary digital landscape, social media has become an integral part of daily life for billions of individuals worldwide. Platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, [more…]
Writing the Middle Ages: Arabic and Persian Perspectives
During the Middle Ages, Arabic and Persian literature emerged as a significant cultural force, shaping not only the intellectual landscape of the Islamic world but [more…]
New Social History: A Fresh Perspective
New Social History emerged as a significant movement in the field of historical scholarship during the late 20th century, particularly gaining traction in the 1960s [more…]
Medieval India’s Historical Voice: Beyond the Sanskrit Tradition
Medieval India, spanning from the 8th to the 18th centuries, was a period marked by a rich tapestry of languages and literary traditions. This era [more…]
The Impact of Social Science Research
Social science research encompasses a broad spectrum of disciplines that study human behavior, societal structures, and the intricate relationships between individuals and their environments. This [more…]
Indo-Persian Chronicles: A Fusion of Cultures
The Indo-Persian chronicles represent a unique confluence of cultures, languages, and histories that emerged primarily during the medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. These chronicles [more…]
Emergence of Social History as a Discipline
The roots of social history can be traced back to the late 19th century, a period marked by significant social upheaval and transformation in Europe [more…]
Sociology and Social Policy: Addressing Inequality and Promoting Equity
Sociology, as a discipline, delves into the intricate web of social relationships, institutions, and structures that shape human behavior and societal norms. It seeks to [more…]