In the realm of design, particularly in user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design, understanding user needs and goals is paramount. This foundational step involves delving deep into the psyche of the target audience to uncover their motivations, preferences, and pain points. By employing various research methodologies such as surveys, interviews, and ethnographic studies, designers can gather qualitative and quantitative data that illuminate the specific requirements of users.
For instance, a mobile banking application may reveal that users prioritize security features and ease of transaction over aesthetic appeal. This insight allows designers to tailor their approach, ensuring that the final product aligns with user expectations. Moreover, creating user personas can be an effective strategy to encapsulate the diverse needs of different segments within the target audience.
These personas serve as fictional representations based on real data, helping designers visualize who they are designing for. For example, a persona representing a busy professional might highlight the need for quick access to account balances and transaction histories, while a persona for a retiree may emphasize the importance of clear instructions and customer support. By keeping these personas in mind throughout the design process, teams can maintain a user-centered focus that drives decision-making and prioritizes features that resonate with actual users.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding user needs and goals is essential for creating a successful interface.
- Creating intuitive and user-friendly interfaces can improve user experience and satisfaction.
- Streamlining navigation and information architecture can help users find what they need quickly and easily.
- Incorporating responsive design for multi-device accessibility ensures a seamless experience across different devices.
- Utilizing visual hierarchy and consistent branding can enhance the overall look and feel of the interface.
Creating Intuitive and User-Friendly Interfaces
An intuitive interface is one that feels natural to users, allowing them to navigate seamlessly without extensive guidance. The design should facilitate an effortless interaction where users can achieve their goals with minimal friction. This can be accomplished through the use of familiar design patterns and conventions that users have come to expect.
For instance, placing navigation menus at the top or left side of a webpage aligns with common user behavior, reducing the learning curve associated with new applications. Additionally, employing clear labeling for buttons and links can significantly enhance usability by providing immediate context for actions. User-friendly interfaces also prioritize accessibility, ensuring that all users, including those with disabilities, can interact with the product effectively.
This involves adhering to established guidelines such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), which outline best practices for making digital content more accessible. For example, incorporating alt text for images allows screen readers to convey information to visually impaired users, while ensuring sufficient color contrast aids those with color blindness. By embracing inclusivity in design, teams not only expand their user base but also foster a sense of belonging among all users.
Streamlining Navigation and Information Architecture
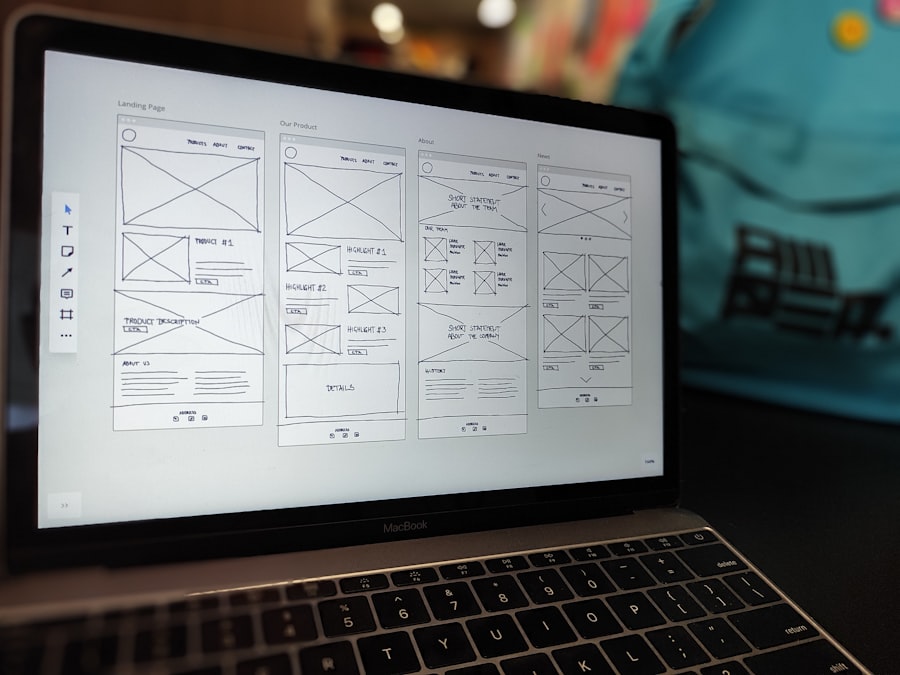
Effective navigation is crucial for guiding users through a digital product and ensuring they can find the information they seek without unnecessary effort. A well-structured information architecture (IA) serves as the backbone of this navigation system, organizing content in a logical manner that reflects user expectations. This can involve categorizing information into clear sections and sub-sections, allowing users to drill down into specific topics without feeling overwhelmed.
For instance, an e-commerce website might categorize products by type, brand, and price range, enabling users to filter their search based on personal preferences. In addition to categorization, designers should consider implementing breadcrumb navigation, which provides users with a visual trail of their path through the site. This not only enhances usability by allowing users to backtrack easily but also reinforces their understanding of the site’s structure.
Furthermore, incorporating search functionality can significantly improve navigation by enabling users to quickly locate specific content or products without having to navigate through multiple layers of menus. By streamlining navigation and refining information architecture, designers create a more efficient user experience that minimizes frustration and maximizes satisfaction.
Incorporating Responsive Design for Multi-Device Accessibility
| Metrics | Results |
|---|---|
| Mobile traffic | 60% |
| Desktop traffic | 40% |
| Responsive design implementation | 100% |
| Page load time on mobile | 3 seconds |
| Page load time on desktop | 2 seconds |
In today’s digital landscape, users access content across a myriad of devices, from smartphones and tablets to laptops and desktops. Responsive design is an approach that ensures a seamless experience regardless of the device being used. This involves creating flexible layouts that adapt to varying screen sizes and orientations while maintaining usability and aesthetic appeal.
For example, a responsive website might rearrange its content into a single column on mobile devices while displaying multiple columns on larger screens, optimizing readability and interaction. Moreover, responsive design goes beyond mere layout adjustments; it also encompasses touch-friendly elements for mobile users. Buttons should be large enough to tap easily without requiring precision, and interactive elements should be spaced adequately to prevent accidental clicks.
Additionally, media queries can be employed to serve different images or styles based on device characteristics, enhancing load times and overall performance. By prioritizing responsive design principles, designers ensure that their products remain accessible and functional across diverse platforms, catering to the evolving habits of modern users.
Utilizing Visual Hierarchy and Consistent Branding
Visual hierarchy is a critical aspect of design that guides users’ attention to the most important elements on a page. By strategically employing size, color, contrast, and spacing, designers can create a clear path for users’ eyes to follow. For instance, larger headlines draw attention first, while smaller text provides supporting details.
This hierarchy not only aids in comprehension but also enhances the overall aesthetic appeal of the interface.
Consistent branding further reinforces visual hierarchy by establishing a cohesive identity across all touchpoints.
This includes maintaining uniformity in color schemes, typography, and imagery throughout the product. When users encounter familiar branding elements—such as logos or color palettes—they are more likely to feel a sense of trust and recognition. For example, a financial institution might use blue tones to evoke feelings of security and reliability while employing consistent typography across its website and mobile app.
By integrating visual hierarchy with consistent branding practices, designers create an engaging experience that resonates with users on both functional and emotional levels.
Conducting User Testing and Iterative Design
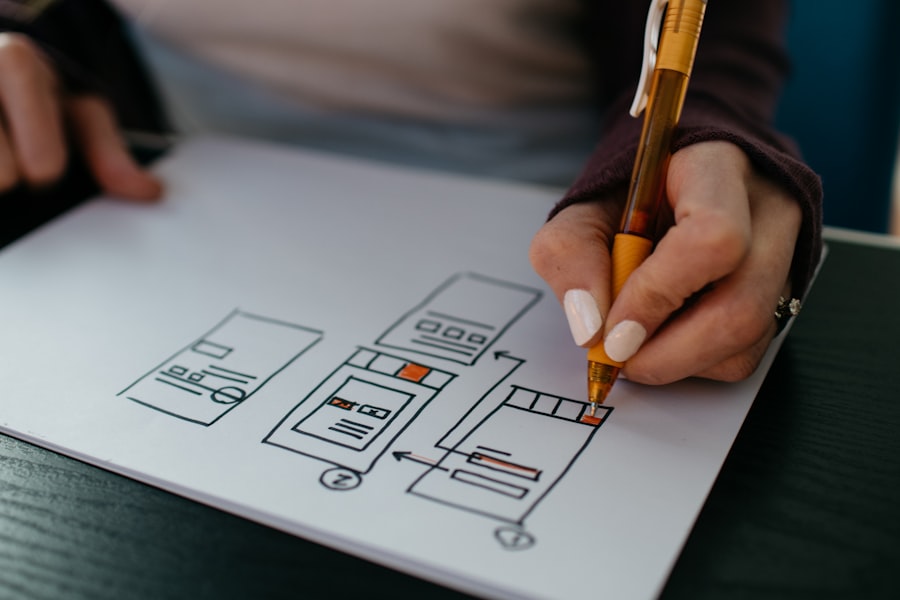

User testing is an essential component of the design process that allows teams to gather direct feedback from real users interacting with their product. This practice can take various forms, including usability testing sessions where participants complete specific tasks while observers note any difficulties encountered. Such insights are invaluable for identifying pain points and areas for improvement that may not have been apparent during the initial design phase.
For instance, if users struggle to locate a particular feature during testing, designers can reassess its placement or visibility within the interface. Iterative design complements user testing by promoting a cycle of continuous refinement based on feedback received. Rather than adhering rigidly to an initial concept, designers should embrace flexibility and be willing to make adjustments as new insights emerge.
This iterative approach fosters innovation by allowing teams to experiment with different solutions before arriving at an optimal design. For example, after conducting user testing on an app’s onboarding process, designers might discover that simplifying instructions leads to higher completion rates. By iterating on designs based on user feedback, teams can create more effective solutions that better meet user needs.
Implementing Personalization and Customization Options
Personalization has become increasingly important in enhancing user experience by tailoring content and features to individual preferences. By leveraging data analytics and user behavior insights, designers can create dynamic experiences that resonate with each user uniquely. For instance, streaming services often recommend shows based on viewing history or allow users to create personalized playlists based on their musical tastes.
This level of customization not only increases user engagement but also fosters loyalty as individuals feel valued by the platform. Customization options empower users further by allowing them to modify aspects of their experience according to their preferences. This could include adjusting themes or layouts within an application or selecting specific features they wish to prioritize on their dashboard.
For example, a project management tool might enable users to choose which metrics are displayed prominently or how tasks are organized within their workspace. By implementing both personalization and customization options, designers create an environment where users feel in control of their experience, leading to greater satisfaction and retention.
Monitoring and Analyzing User Feedback for Continuous Improvement
The journey of enhancing user experience does not end with the launch of a product; it requires ongoing monitoring and analysis of user feedback to ensure continuous improvement. Various tools such as analytics platforms can provide valuable insights into user behavior patterns—highlighting areas where users may struggle or disengage from the product.
In addition to quantitative data from analytics tools, qualitative feedback gathered through surveys or direct user interviews can provide context for understanding user experiences more deeply. This dual approach allows teams to triangulate data points and develop comprehensive strategies for addressing identified issues. Regularly revisiting user feedback ensures that products evolve alongside changing user needs and preferences—ultimately fostering a culture of continuous improvement that keeps the user experience at the forefront of design efforts.
By committing to this ongoing process of monitoring and analysis, organizations can remain agile in adapting their offerings to meet ever-evolving demands in the digital landscape.
In the ever-evolving field of UX Design, understanding the cultural and historical context of users can significantly enhance the design process. An interesting perspective on this can be found in the article titled “Exploring the Intersection of Mathematics, Education, History, and Culture.” This piece delves into how cultural and historical factors influence educational practices, which can be paralleled to how these factors affect user experience in design. By integrating such insights, UX designers can create more inclusive and effective interfaces that resonate with diverse user groups. For more information, you can read the full article here.





















+ There are no comments
Add yours