The journey of abstraction in art is a fascinating narrative that spans centuries, evolving from the representational forms of early civilizations to the non-objective expressions of the 20th century. The roots of abstraction can be traced back to ancient cultures, where artists began to simplify and stylize their representations of the world around them. For instance, the geometric patterns found in ancient Egyptian art and the symbolic motifs in African tribal art reflect an early inclination towards abstraction.
These early forms were not merely decorative; they served spiritual and cultural purposes, conveying complex ideas through simplified shapes and forms. As art progressed through the Renaissance and into the modern era, the notion of abstraction began to take on new meanings. The Impressionists, for example, moved away from precise representation to capture the essence of a moment through light and color.
This shift laid the groundwork for later movements such as Cubism and Futurism, which further dismantled traditional perspectives. Artists like Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque deconstructed objects into geometric shapes, challenging viewers to engage with art in a more conceptual manner. By the time the 20th century arrived, abstraction had fully emerged as a dominant force in the art world, with movements like Abstract Expressionism leading the charge.
Artists such as Jackson Pollock and Mark Rothko explored the emotional and psychological dimensions of color and form, creating works that prioritized personal expression over representational accuracy.
Key Takeaways
- Abstraction in art has a long history, dating back to the early 20th century with artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Piet Mondrian.
- Modern design has been heavily influenced by abstraction, with its emphasis on simplicity, minimalism, and geometric shapes.
- Abstract art can be interpreted in many different ways, as it often lacks a clear subject or narrative, allowing viewers to bring their own meaning to the artwork.
- Abstract art can evoke a wide range of emotions and feelings, as it often relies on color, form, and texture to convey its message.
- Abstraction in photography involves capturing the essence of a subject rather than its literal representation, often through techniques like close-ups, blurring, and unconventional angles.
The Influence of Abstraction in Modern Design
Abstraction has permeated various facets of modern design, influencing everything from graphic design to product development. In graphic design, abstraction is often employed to create visual identities that resonate on an emotional level. Designers utilize simplified shapes, bold colors, and minimalistic layouts to convey messages that transcend language barriers.
For instance, the iconic logo of Apple Inc. is a prime example of how abstraction can encapsulate a brand’s ethos—its sleek, minimalist design communicates innovation and sophistication without relying on literal imagery. In product design, abstraction plays a crucial role in shaping user experiences.
Designers often strip away unnecessary details to focus on functionality and aesthetics, resulting in products that are both visually appealing and intuitive to use. The work of designers like Dieter Rams, known for his philosophy of “less but better,” exemplifies this approach. His designs for Braun products emphasize clean lines and functional forms, demonstrating how abstraction can enhance usability while maintaining a strong visual identity.
This trend towards abstraction in design reflects a broader cultural shift towards simplicity and clarity in an increasingly complex world.
Understanding Abstract Art: What Does it Mean?
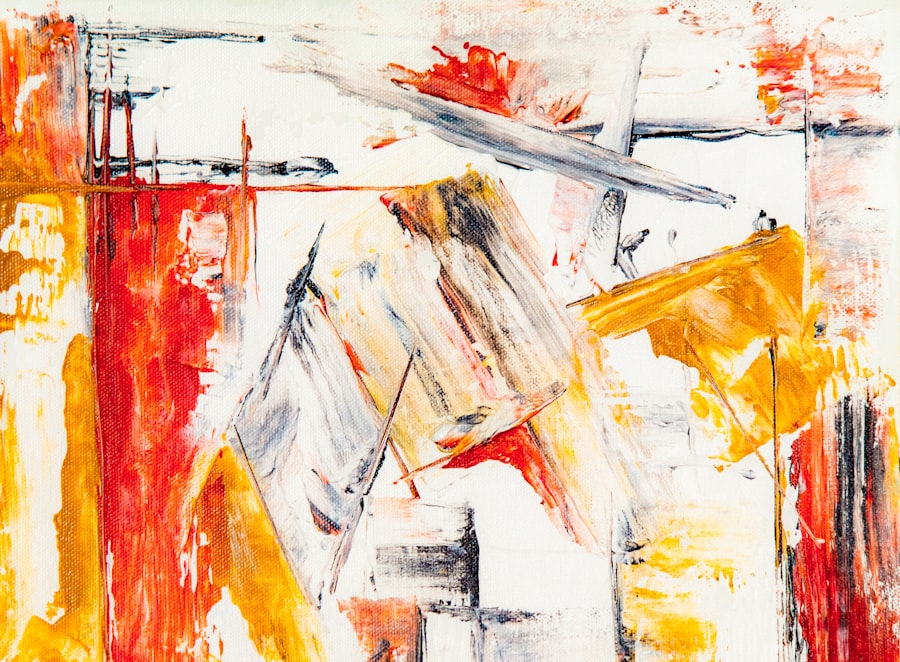

Understanding abstract art requires a departure from traditional notions of representation and an embrace of subjective interpretation. Unlike figurative art that depicts recognizable subjects, abstract art often prioritizes color, form, and texture as primary elements of expression. This shift invites viewers to engage with the artwork on a more personal level, allowing them to derive meaning based on their own experiences and emotions. For instance, a canvas splashed with vibrant colors may evoke feelings of joy or chaos, depending on the viewer’s perspective.
The meaning behind abstract art can also be influenced by the artist’s intent. Many abstract artists aim to convey specific emotions or concepts through their work, using color theory and compositional techniques to guide the viewer’s response. For example, Wassily Kandinsky believed that colors had inherent emotional qualities; he used this belief to create compositions that resonated with viewers on a spiritual level.
In this way, abstract art becomes a dialogue between the artist and the audience, where meaning is not fixed but rather fluid and open to interpretation.
Exploring the Emotions and Feelings in Abstract Art
| Emotion | Artwork | Artist |
|---|---|---|
| Joy | Composition VII | Vasily Kandinsky |
| Fear | The Scream | Edvard Munch |
| Sadness | Blue Nude | Henri Matisse |
| Love | The Kiss | Gustav Klimt |
One of the most compelling aspects of abstract art is its ability to evoke a wide range of emotions and feelings. The use of color is particularly significant in this regard; different hues can elicit distinct emotional responses. For instance, warm colors like red and orange are often associated with energy and passion, while cooler tones like blue and green can evoke calmness or introspection.
Artists harness these emotional qualities to create works that resonate deeply with viewers, inviting them to explore their own feelings in relation to the artwork. Moreover, the physicality of abstract art—its textures, shapes, and forms—can also contribute to emotional engagement. The gestural brushstrokes of an Abstract Expressionist painting may convey a sense of urgency or spontaneity, while smooth surfaces might evoke tranquility or contemplation.
This interplay between form and emotion allows abstract art to transcend mere visual representation; it becomes a conduit for exploring complex human experiences. For example, Mark Rothko’s large color field paintings are renowned for their ability to evoke profound emotional responses, drawing viewers into a meditative state as they contemplate the interplay of color and light.
The Use of Abstraction in Photography
Abstraction in photography offers a unique lens through which to view the world, transforming ordinary subjects into extraordinary compositions. Photographers often employ techniques such as blurring, cropping, and unconventional angles to create images that challenge traditional perceptions. This approach allows them to focus on elements like light, shadow, and texture rather than merely documenting reality.
For instance, the work of photographers like Aaron Siskind exemplifies this trend; his abstract photographs capture the essence of surfaces and forms, inviting viewers to appreciate beauty in unexpected places. Additionally, digital manipulation has expanded the possibilities for abstraction in photography. Artists can now alter images in ways that were previously unimaginable, creating surreal landscapes or dreamlike compositions that defy logic.
This manipulation can serve as a commentary on reality itself, prompting viewers to question their perceptions of truth and representation. The work of contemporary photographers such as Thomas Ruff illustrates this intersection of technology and abstraction; his digitally altered portraits challenge notions of identity while exploring the boundaries between reality and illusion.
The Intersection of Abstraction and Nature
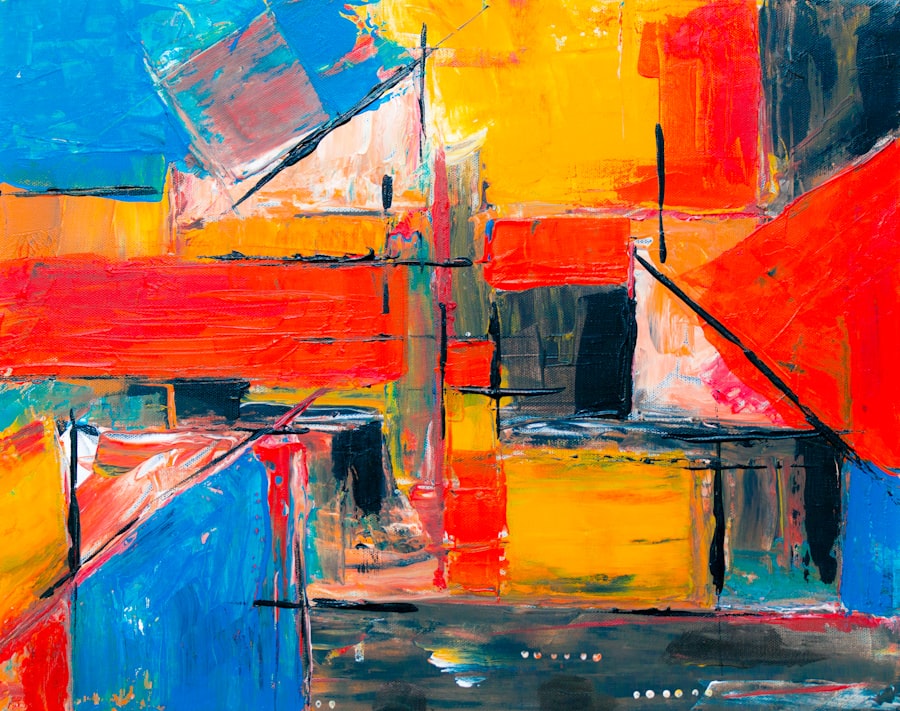

The relationship between abstraction and nature is rich and multifaceted, as artists often draw inspiration from the natural world while simultaneously distilling its essence into abstract forms.
This approach allows them to explore themes such as impermanence, transformation, and interconnectedness without being confined by literal representation.
For example, artists like Georgia O’Keeffe have famously abstracted floral forms into bold shapes and colors that evoke both the physicality of flowers and their emotional resonance. Her work transcends mere botanical representation; it invites viewers to experience nature’s beauty on a deeper level. Similarly, contemporary artists like Olafur Eliasson create immersive installations that blur the boundaries between nature and abstraction.
His works often incorporate natural elements such as light and water to create experiences that challenge viewers’ perceptions of their environment.
The Role of Abstraction in Contemporary Architecture
Abstraction has become increasingly prominent in contemporary architecture, where it serves as both an aesthetic choice and a conceptual framework for design. Architects often employ abstract forms to create structures that challenge conventional notions of space and function. This approach allows for innovative designs that prioritize not only visual impact but also environmental sustainability and social engagement.
One notable example is the work of Zaha Hadid, whose architectural designs are characterized by fluid forms and dynamic lines that defy traditional architectural conventions. Her buildings often appear as if they are in motion, reflecting a sense of energy and vitality that resonates with their surroundings. This emphasis on abstraction allows architects like Hadid to create spaces that foster interaction and engagement among users while pushing the boundaries of what architecture can be.
Many contemporary architects are embracing simplicity in their designs, focusing on essential forms that harmonize with their environments. This trend not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also promotes ecological responsibility by minimizing material waste and energy consumption.
The Future of Abstraction: New Trends and Innovations
As we look towards the future of abstraction in art and design, several emerging trends signal exciting possibilities for innovation and exploration. One notable trend is the increasing integration of technology into abstract practices. Digital tools are enabling artists and designers to experiment with new forms of expression that were previously unattainable.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are opening up new avenues for immersive experiences that blend abstraction with interactivity. Additionally, there is a growing interest in collaborative practices that bring together artists from diverse disciplines to explore abstraction in novel ways. Cross-disciplinary collaborations between visual artists, musicians, dancers, and technologists are resulting in innovative projects that challenge traditional boundaries between art forms.
These collaborations not only enrich the creative process but also foster dialogue about the role of abstraction in contemporary culture. Furthermore, as society grapples with complex global issues such as climate change and social justice, abstraction may serve as a powerful tool for reflection and activism. Artists are increasingly using abstract forms to address pressing concerns while encouraging viewers to engage with these issues on an emotional level.
This intersection of abstraction with social consciousness suggests a future where art continues to evolve as a means of exploring both personal expression and collective responsibility. In conclusion, abstraction remains a dynamic force within art and design, continually reshaping our understanding of creativity across various disciplines. As we navigate an ever-changing world filled with complexity and uncertainty, abstraction offers a lens through which we can explore new ideas, emotions, and connections—inviting us all to engage with art in profound ways.
If you are interested in exploring a rigorous approach to philosophical inquiry, you may want to check out the article Analytic Philosophy: A Rigorous Approach to Philosophical Inquiry. This article delves into the principles and methods of analytic philosophy, which emphasizes clarity, logic, and precision in philosophical analysis. It provides a comprehensive guide to understanding this philosophical approach and its significance in the field of philosophy.


















+ There are no comments
Add yours